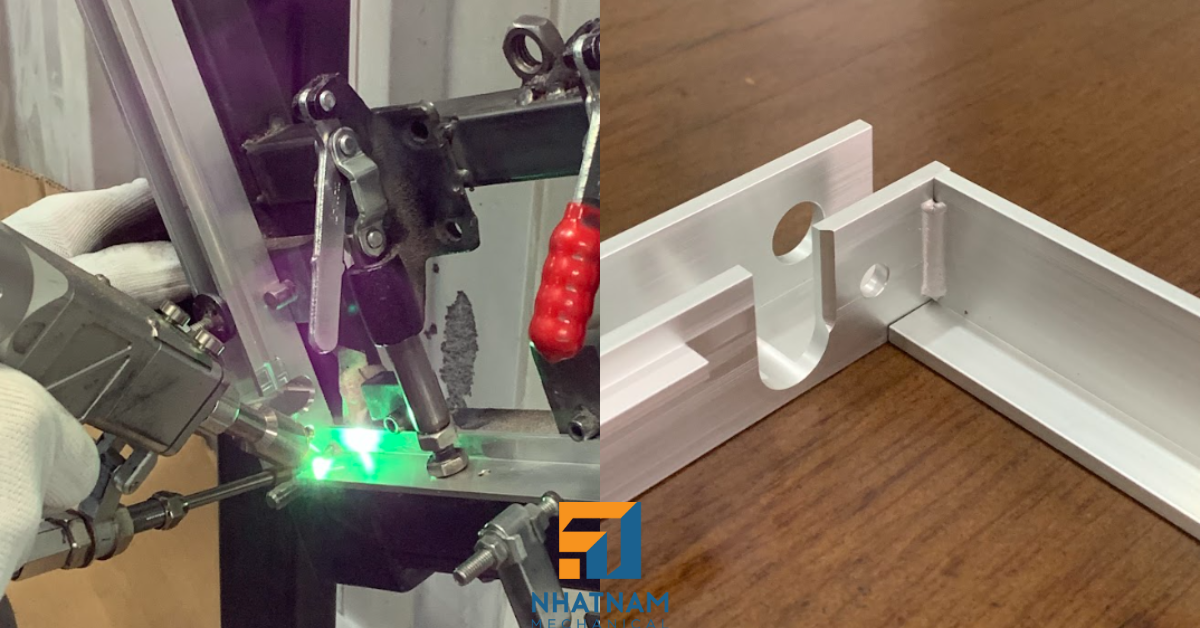
Ensuring the quality of welds in sheet metal processing not only helps maintain structural strength but also directly affects the life and safety of the product. This article presents methods of weld inspection through visual observation and the use of specialized equipment, analyzes the advantages and disadvantages of each method, and makes recommendations for application depending on each production stage.
1. What is a Weld?
A weld is a joint between two or more metal parts that are joined by heating and/or applying pressure. In sheet metal production, the quality of the weld determines the durability, aesthetics, and load-bearing capacity of the product. Therefore, weld inspection is a mandatory step to detect defects such as cracks, porosity, slag inclusion, or lack of penetration.

2. Common Types of Defects in Sheet Metal Welds
- Cracks: Pose serious risks and can develop over time, potentially compromising the structural integrity.
- Porosity: Caused by gas trapped in the molten metal.
- Incomplete fusion: The weld does not fully bond to the base metal.
- Undercut (Sagging): Metal is removed from the area adjacent to the weld, reducing strength.
- Slag inclusion: Welding slag not thoroughly cleaned before or after welding becomes trapped in the weld.
3. Visual Inspection Methods
3.1 Principle
Visual inspection is based on using natural or artificial light, combined with tools such as magnifying glasses, weld gauges, and inspection lamps.
3.2 Inspection Procedure
- Clean the weld surface.
- Observe under proper lighting conditions.
- Measure the shape, height, and width of the weld.
- Compare with technical standards (e.g., AWS D1.1, ISO 5817).
3.3 Advantages
- Fast and cost-effective.
- Suitable for preliminary or in-process inspections.
- Non-destructive to the specimen.
3.4 Limitations
- Relies on the experience and skill of the inspector.
- Cannot detect internal or subsurface defects.
4. Instrumental Testing Methods (Non-Destructive Testing – NDT)
4.1 Ultrasonic Testing (UT)
- Mechanism: Uses ultrasonic waves that reflect from defects within the weld.
- Advantages: Detects internal flaws.
- Applications: Ideal for thick welds or where high reliability is required.

4.2 Radiographic Testing (RT)
- Mechanism: Uses X-rays or gamma rays to image the internal structure of the weld.
- Advantages: Produces clear images of internal defects.
- Disadvantages: High cost and requires strict radiation safety measures.
4.3 Magnetic Particle Testing (MT)
- Mechanism: Applied to ferromagnetic metals, using magnetic fields to detect surface or near-surface cracks.
- Advantages: Fast and effective for surface-related defects.
4.4 Liquid Penetrant Testing (PT)
- Mechanism: Involves applying a dye penetrant to the surface, which seeps into surface-breaking defects, followed by the application of developer powder to reveal indications.
- Advantages: Easy to use and applicable to a wide range of materials.
- Limitations: Only effective for detecting surface-breaking defects.

5. Comparison and Recommendations
| Criteria | Visual (VT) | Instrumental (NDT) |
|---|---|---|
| Detectability | Surface defects only | Surface and internal defects |
| Cost | Low | Medium to high |
| Technical requirements | Moderate (basic training) | High (specialized training, certification) |
| Practical applications | Fast, in-process inspection | Final inspection, critical components |
Recommendations:
- Visual testing (VT) should be conducted throughout the production process to detect surface-level defects early.
- Non-destructive testing (NDT) should be applied to critical products, load-bearing welds, or when required by customers or applicable standards.
6. Conclusion
Weld quality assessment is an indispensable step in the sheet metal manufacturing process. Combining visual inspection and non-destructive testing (NDT) methods ensures optimal inspection efficiency, guaranteeing that the final product meets technical standards, aesthetic requirements, and long-term durability.

At Nhat Nam Mechanical, we offer high-quality sheet metal welding services backed by a team of experienced welders and a rigorous quality control system. All welds are performed and inspected in accordance with AWS D1.1 – Structural Welding Code – Steel, ensuring precision, structural integrity, and a professional finish. We apply a comprehensive range of inspection methods—from visual testing to advanced non-destructive techniques—to give customers confidence in the safety and longevity of every product. With state-of-the-art equipment, flexible manufacturing capabilities, and a strong commitment to on-time delivery, Nhat Nam has become a trusted partner of many domestic and international clients in the field of mechanical engineering.

NHAT NAM MECHANICAL CO., LTD contact information: House No. 36, Garland – Phuoc Dien, 72 Duong Dinh Hoi, Phuoc Long B Ward, District 9, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam.
Contact Japan
Email: tranquy@cokhinhatnam.vn
Tel: +84 938 771 508
Contact English
Email: marketing@cokhinhatnam.vn
Tel: +84 964 092 079
Contact Vietnam
Email: vinhnt@cokhinhatnam.vn
Tel: +84 964 084 479
