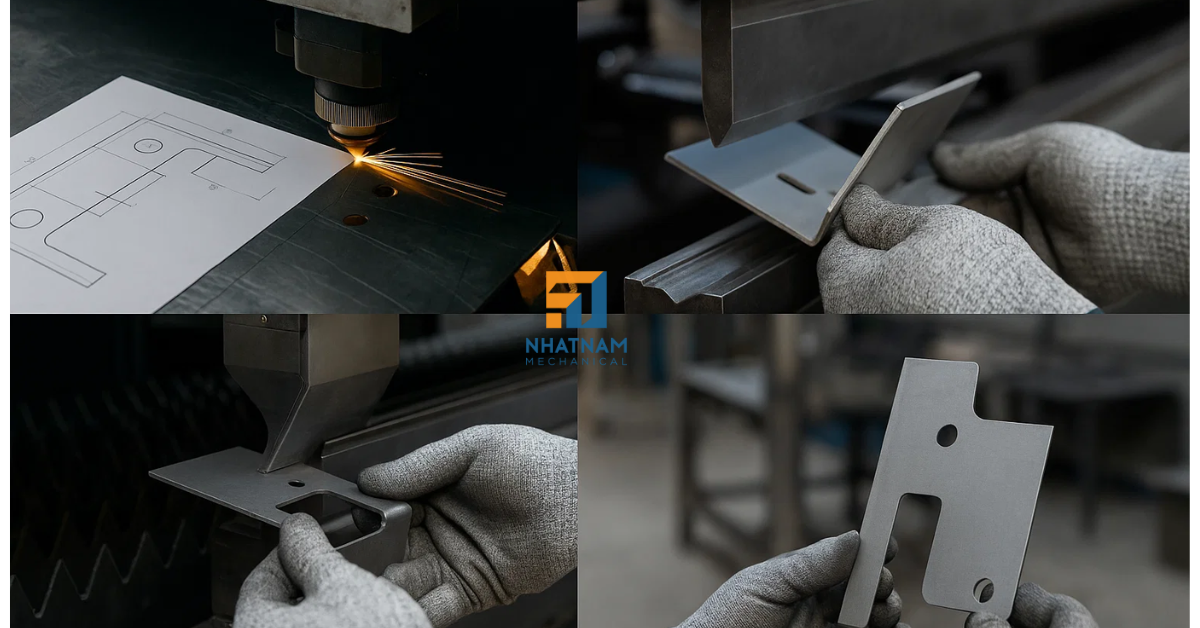
In the past, sheet metal fabrication was largely done manually, requiring a lot of time, manpower, and highly skilled labor. Today, thanks to the rapid development of technology, modern factories around the world are completely changing the way sheet metal products are manufactured — making each step faster, more precise, and more efficient.
In this article, we’ll explore how modern factories have improved every stage of the sheet metal fabrication process — from design, cutting, bending, and welding to surface finishing — and why these advancements are reshaping global manufacturing standards.
1. Overview: Basic Steps in the Sheet Metal Fabrication Process
Before discussing the improvements, let’s review the main steps in the traditional sheet metal fabrication process:
- Design & Material Selection: Engineers create 2D or 3D drawings and select suitable materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, or carbon steel.
- Metal Cutting: Using laser, plasma, or waterjet cutters to shape parts.
- Forming/Bending: Using presses or press brakes to form and bend metal into the required angles and dimensions.
- Welding & Assembly: Joining parts together to form assemblies or complete products.
- Surface Treatment: Applying powder coating, plating, or polishing to enhance aesthetics and corrosion resistance.
- Inspection & Delivery: Ensuring the finished products meet technical standards before delivery.
These are the foundations of every sheet metal fabrication shop — but what truly sets modern factories apart is how they optimize each step.
2. Improvements in Design and Material Planning
All improvements begin at the design stage. Modern factories use CAD/CAM software and 3D simulation to create digital models and predict actual results before production.
Thanks to these tools, engineers can:
- Detect and eliminate design errors early.
- Optimize material selection and cutting layouts.
- Reduce material waste and overall production costs.
In particular, automatic nesting software helps maximize sheet utilization — a critical factor in mass production.
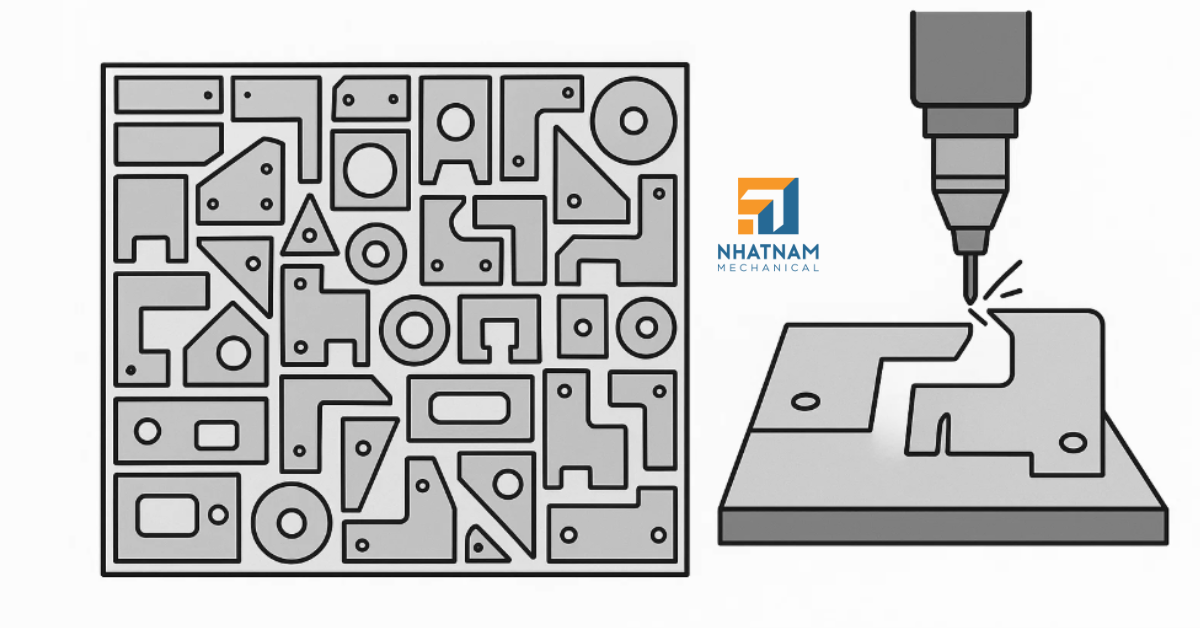
3. Precise Metal Cutting with Modern Technology
Cutting is one of the most important steps in sheet metal fabrication.
Instead of traditional mechanical cutting, factories now use fiber laser cutting technology, which offers:
- High precision (tolerances within ±0.1 mm).
- Smooth cutting edges that require no secondary processing.
- Faster cutting speeds, suitable for various materials and thicknesses.
Additionally, automatic material loading and unloading systems allow the cutting machines to operate continuously — minimizing downtime and reducing operator risks.
4. Bending and Forming with CNC Press Brakes
In the bending process, accuracy and repeatability are key.
Modern factories use CNC press brakes equipped with:
- Automatic angle-measuring sensors.
- Real-time force feedback systems.
- Memory storage for bending parameters of each product.
As a result, each part achieves the correct bending angle, dimensions, and tolerances according to the design.
Moreover, saving bending formulas allows faster, more consistent mass production.

5. Automated Welding and Assembly
In the past, welding quality relied heavily on the operator’s skills.
Today, automated welding robots have become an inevitable trend.
MIG/TIG robots can:
- Maintain uniform and strong welds.
- Operate continuously, minimizing human error.
- Reach difficult angles with greater precision.
Additionally, custom-designed fixtures help position parts accurately and reduce assembly errors during welding.
6. Automated and High-Quality Surface Finishing
Surface finishing is a crucial step that determines both the appearance and durability of the product.
Modern factories use automated powder coating, polishing, and anodizing systems that help:
- Control coating thickness uniformly.
- Ensure consistent color and gloss.
- Minimize manual inconsistencies.
Automatic systems for temperature and drying time control also ensure that coatings achieve higher durability and better scratch resistance.

7. Digital Quality Inspection
Today, inspection is performed using 3D scanning systems, CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machines), or even AI-powered inspection systems that can detect minute defects.
These technologies ensure that each part meets design tolerances and also record data for product traceability — an increasingly important requirement when working with international clients.
8. Benefits of Process Improvement
By optimizing each stage of production, factories can achieve:
- Higher productivity and reduced production time.
- Lower costs through material savings and fewer errors.
- Consistent quality that meets international standards.
- Faster delivery and improved accuracy.
- Enhanced reputation and customer satisfaction.
9. Real-Life Example: Nhat Nam Mechanical
At Nhat Nam Mechanical, we apply modern technology in every stage of sheet metal processing — from fiber laser cutting and CNC bending to robotic welding and automated surface finishing.
Thanks to continuous investment in equipment and process optimization, Nhat Nam ensures that each product meets high precision, stable quality, and cost efficiency, making us a trusted partner for customers both in Vietnam and abroad.

